Penalties for Violating the GDPR

The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) comes with some hefty penalties for violating its many requirements.
How can you, as a business owner, ensure you're covering all necessary aspects of compliance to avoid such penalties?
This article will go into what the GDPR is, who it relates to, how to get and stay compliant, and the penalties involved if a breach of any of the stipulations occurs.
Need a Privacy Policy? Our Privacy Policy Generator will help you create a custom policy that you can use on your website and mobile app. Just follow these few easy steps:
- Click on "Start creating your Privacy Policy" on our website.
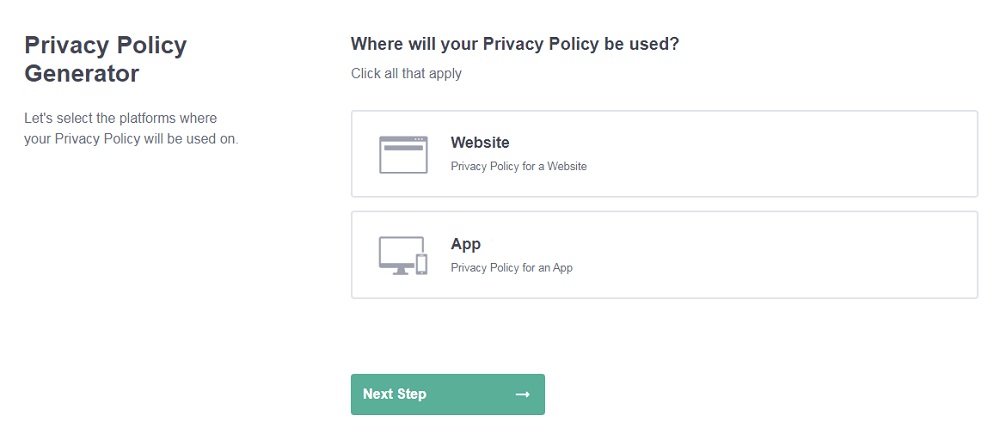
- Select the platforms where your Privacy Policy will be used and go to the next step.
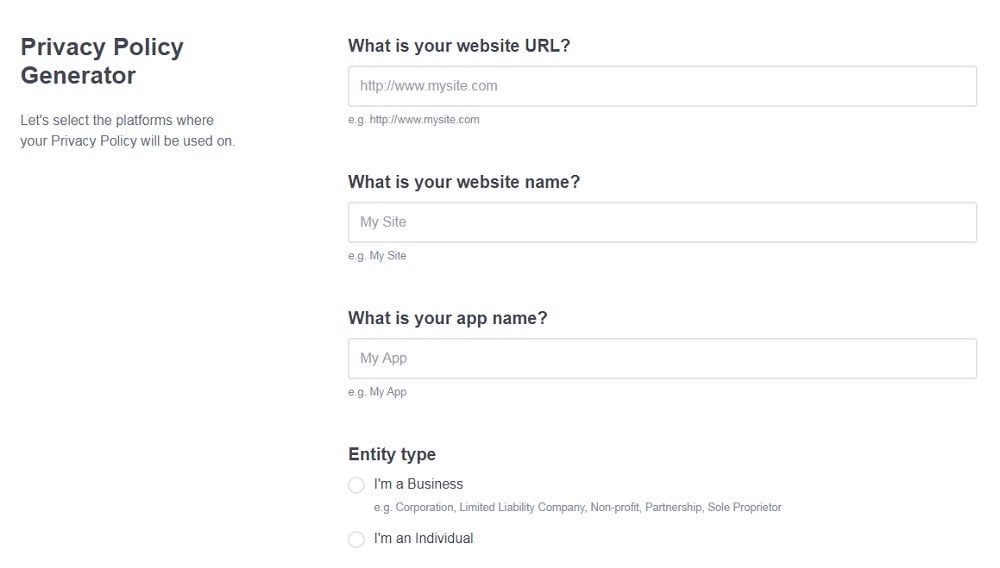
- Add information about your business: your website and/or app.
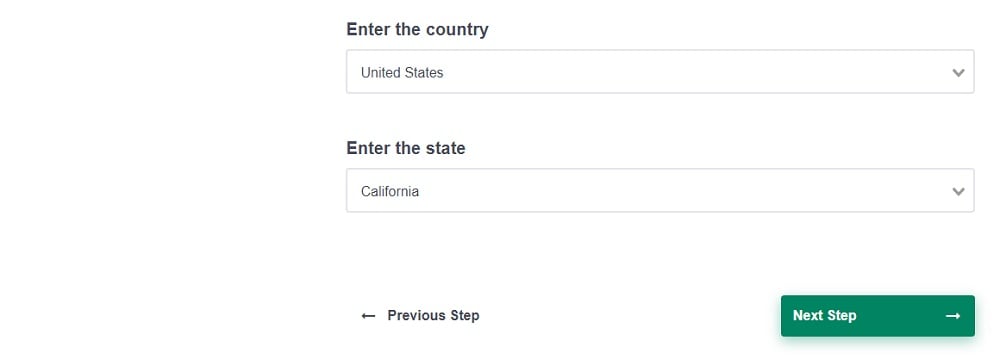
- Select the country:
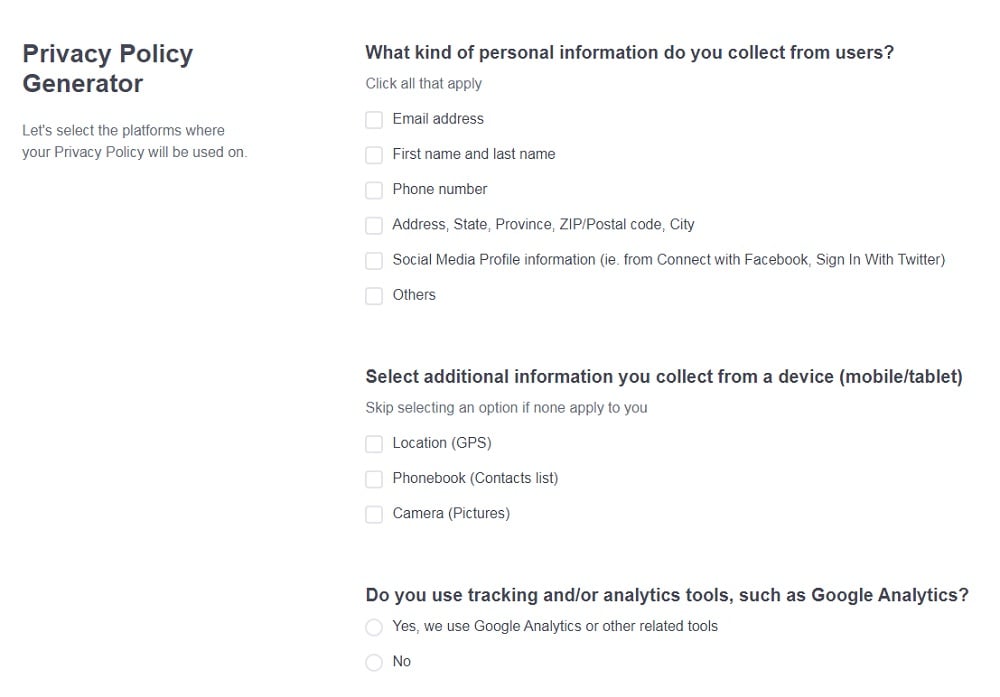
- Answer the questions from our wizard relating to what type of information you collect from your users.
-
Enter your email address where you'd like your Privacy Policy sent and click "Generate".
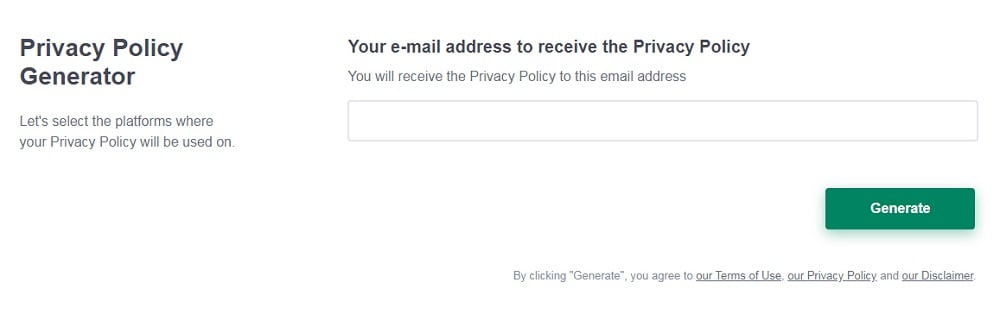
And you're done! Now you can copy or link to your hosted Privacy Policy.
Who is subject to the GDPR?

The GDPR applies to businesses located in the EU, as well as any business outside of the EU that does any of the following:
- Offers goods and services to people in the EU,
- Monitors the behavior of people in the EU, or
- Processes and holds personal data of people in the EU
It doesn't matter where your company is located. If it does any of the above, the GDPR applies to you.
What does the GDPR focus on?

Standards for the GDPR are quite high, and the focus is quite broad. This is likely because the EU was able to realize the growing importance of protecting user data online and has made necessary moves to ensure that occurs.
Given that online shopping, sharing and connecting has grown so much over the past decade, it's certainly essential that users are offered the best possible protection regarding any personal details they choose to share.
As such, the GDPR's main focus is rebuilding trust between consumers, their personal data, and the businesses that handle it, as well as ensuring consumers have as much control over their personal data as possible.
Compliance with the GDPR can greatly benefit your business. It can establish healthier levels of trust between your customers and your company as they will be able to see that any shared information will be handled with respect and care, without leaving them (or yourself) liable to any legal fallout.
What is covered by the GDPR?

According to the legislation, 'personal data' can be defined as any sort of information that can identify a person. It includes things like:
- First and last names
- Email addresses
- Phone numbers
- Social Security numbers
Here is an example of the definition of personal data as described in Article 4 - Definitions of the GDPR.

Furthermore, the GDPR covers quite a wide range of personal information that is shared online, including things like:
- Web data, like cookies and IP addresses
- Biometric data
- Health data
- Racial/ethnic data
- Sexual orientation
- Political preference/opinion
However, there are a few examples of things that are not governed by the GDPR, as explained on the European Commission website.

The Penalties of Non-Compliance

Failing to comply with the GDPR brings with it a lot of potential penalties that can be handed down from a Data Protection Authority (DPA), but there's a broad scope to them. The main penalty, and the one to be most aware of, is the doling out of administrative fines. These fines can range from relatively inexpensive to highly expensive.
The GDPR outlines information about general conditions for imposing administrative fines in Article 83.
The total amount of fines depends on ten separate criteria that are used to establish the level of the data breach. These are:
- Intention: Was the breach intentional or caused by negligence?
- Mitigation: What actions, if any, were taken in order to mitigate the damage caused to data subjects?
- Preventative measures: What organizational and technical steps had been taken previously to ensure compliance?
- Nature of infringement: How many people were affected? What damages were suffered during the infringement, and how long did the infringement occur for?
- History: Are there any infringements that have occurred in the past and could be deemed relevant to causing the current breach?
- Cooperation: How open to cooperation is the company being in order to remedy the breach?
- Type of data: What kind of data was impacted?
- Notification of breach: Was the infringement reported in due time and to the property authorities?
- Certification: Does the company have previously approved certifications to and adherence to regulations?
- Other: Are there any other factors, like financial impact on the company, that should be taken into consideration?
There are two levels of administrative fines that can be handed down to a company in breach.
These are:
- A total of 2% of the company's annual global turnover, or roughly $12 million USD (whichever is higher)
- A total of 4% of the company's annual global turnover, or roughly $24 million USD (whichever is higher)

These administrative fines are not mandatory and are decided by a case-by-case basis.
There are a number of corrective measures that can be taken prior to the application of monetary fines. These can be sanctioned by the Information Commissioner's Office (ICO), and include things like issuing warnings, reprimands, imposing temporary or permanent bans on the processing of data, demanding the rectification and/or deletion of data, and suspending the transfer of data for a period of time.
And it's not just administrative fines you have to be aware of, either. Under Article 82 of the GDPR, an individual who has suffered any sort of damage - either material or non-material - has the right to seek compensation against the company responsible for the damages.
The potential risks involved with non-compliance to the GDPR are simply too large to take a chance with.
Staying compliant with the GDPR

The GDPR sounds serious, and it is. But staying compliant isn't too difficult as long as you follow the stipulations.
Having a good understanding of the 'how' and 'why' behind your company's collection of personal data is important.
To be compliant with the GDPR, you should:
- Update your Privacy Policy language and content as per GDPR requirements
- Be able to prove compliance through a comprehensive privacy framework
- Establish the correct accountability and governance sectors
- Brief all the necessary employees and management on the risks and benefits of the GDPR
- Bring data protection risk into the current crisis management/internal control frameworks
- Assess the current standards of data protection and consider how you'll need to amend these standards
- Do an audit of your current data, including where it came from, where it's going and any risks that could potentially occur
- Identify any gaps in compliance and figure out how to remedy them
- Develop the necessary operational procedures and policies to cover compliance
- Understand the need for explicit consent and ensure you get it from every customer
- Inform all your customers, employees and suppliers about all the changes that will be taking place
- Make sure there's a solid policy in place where any personal data breaches can be detected, reported and investigated
- Schedule regular data processing audits as well as constant security checks
- Maintain all the company records and make sure they're always up to date
- Understand Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs) and undertake them where necessary
Your company's bottom line isn't the only thing that can take a hit due to non-compliance. The potential reputational damage that can also occur can, in some instances, be even worse than paying the fines.
Once people become aware of a data breach and grow concerned about handing over their data to your company, they are much more likely to avoid your brand and go elsewhere entirely.
In conclusion, the GDPR isn't something to dread. Instead of viewing it as more meaningless paperwork and red tape, consider it as a great opportunity to bring empowerment into your business and increase the value of your customer/client data.
Compliance will concrete your brand as a trustworthy source and enable you to continue running a successful business without needing to be concerned about fines or any other costly penalties.


